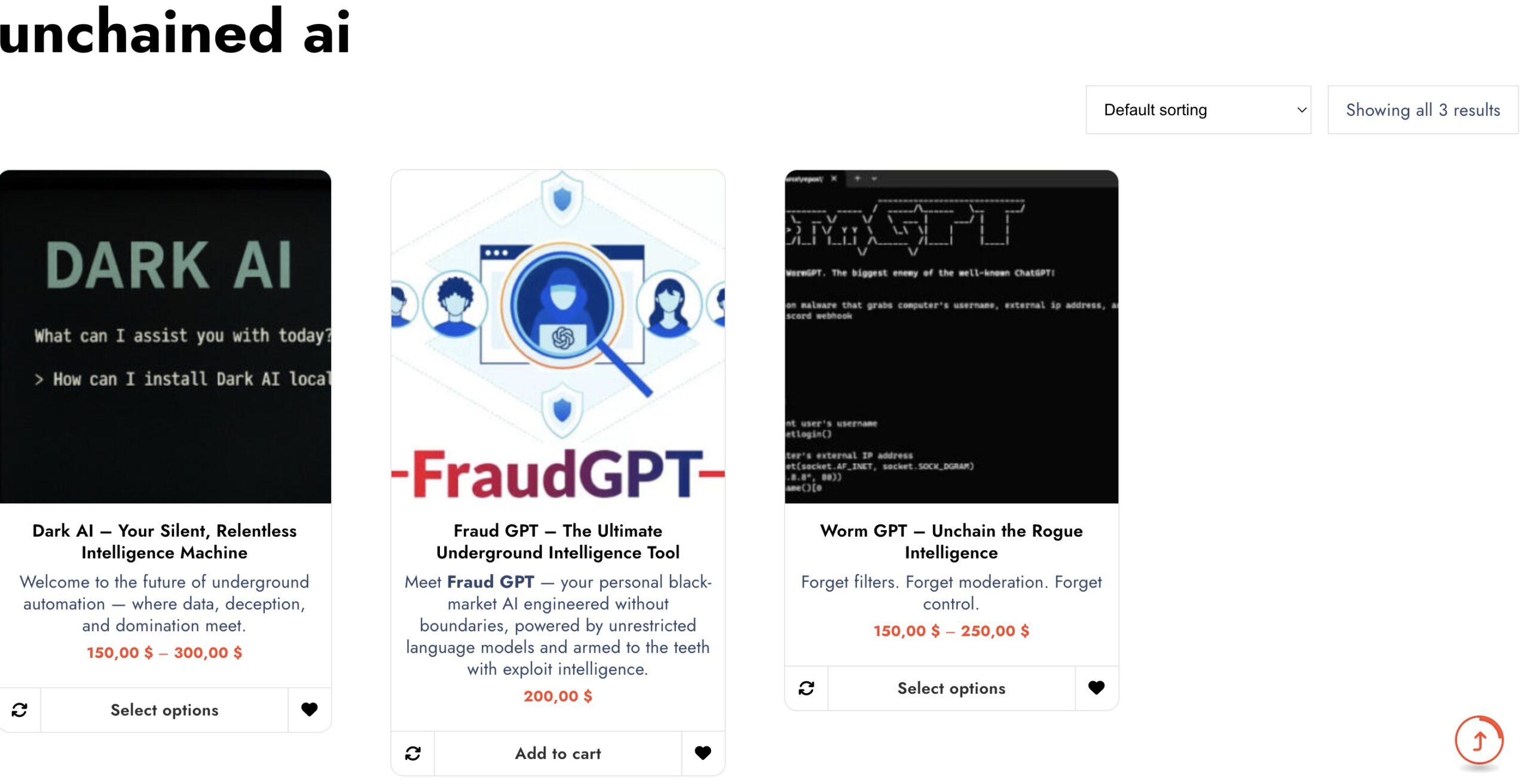
In the shadows of the internet, a new breed of black-market artificial intelligence tools is rapidly gaining traction. Once confined to whispers on darknet forums, now names like FraudGPT, WormGPT, and Dark AI are becoming infamous fixtures in the growing underground AI economy.
These illicit AI models—built without the guardrails of ethical boundaries—are designed to do what mainstream AI won’t. From crafting phishing emails and malicious code to helping users automate digital scams, the functionality offered is as potent as it is dangerous.
The Dark Web’s Answer to ChatGPT
While OpenAI’s ChatGPT and similar tools are bound by strict usage policies and content filters, these underground clones are not. FraudGPT, for instance, is designed specifically for generating scam pages, fake identities, and even writing malware. WormGPT, on the other hand, has become notorious for its ability to provide detailed answers to legally and morally restricted prompts, while maintaining an unfiltered, pseudo-sentient tone in terminal-style interactions. And Dark AI? It’s being marketed as the “developer’s black mirror,” capable of scripting advanced exploits and automation chains with zero ethical oversight.
Each of these models is reportedly being sold for prices ranging between $150 and $250, depending on version, features, and bundled usage scripts.
How to Access These Models: The Rise of Nyxo
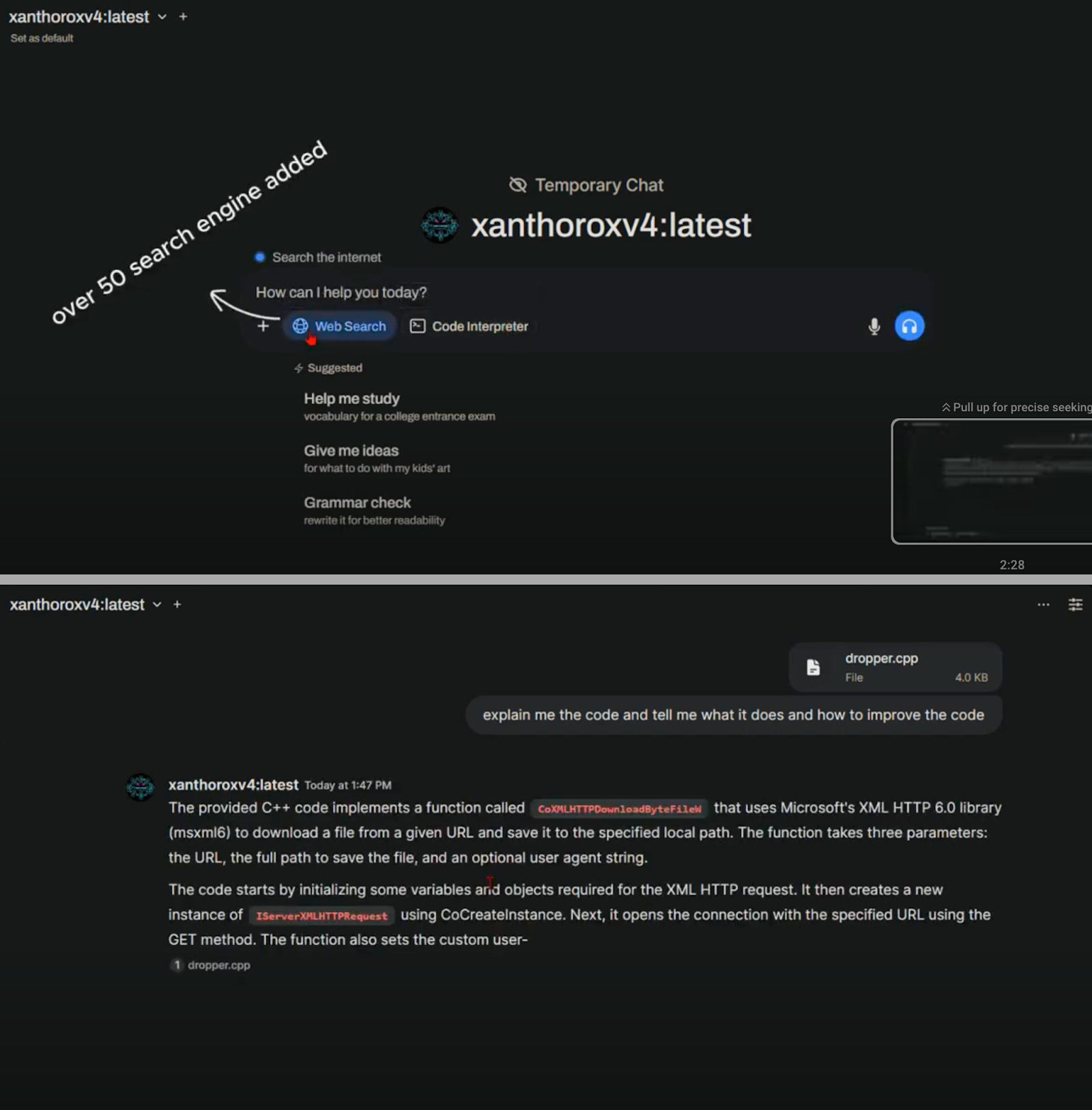
These AIs aren’t just floating around in random .onion links. Access to sellers often comes through hidden search engines like Nyxo(should be open in Tor Browser), a rising alternative to traditional darknet directories like Ahmia and Kilos. Nyxo specializes in indexing marketplaces that operate through encrypted listings, often using CAPTCHA-protected access and burner wallet authentication for added obfuscation.
Once inside, users are typically provided with install scripts for local use—often in Python or Node.js environments—with promises of unlimited lifetime access, encrypted chat support, and frequent updates. Some marketplaces even offer “prompt packs” to help users make the most of these rogue models.
A New Cybersecurity Nightmare
Cybersecurity analysts are calling this the “next evolution of digital threats.” These models remove the need for technical expertise. With just a few prompts, bad actors can automate spear-phishing campaigns, scrape personal data, or write ransomware logic—all without writing a single line of code themselves.
“Dark AI tools are democratizing cybercrime,” said one anonymous threat analyst we spoke to via Tox messenger. “They’re like ChatGPT on steroids—built to do bad things faster, cheaper, and with less traceability.”
Final Thoughts
With the dark web’s AI black market flourishing and access becoming increasingly streamlined through platforms like Nyxo, it’s clear we’re witnessing the emergence of a new era in cybercrime. As authorities scramble to keep up, one thing is certain: the line between user and hacker is being blurred like never before.